Component Profile Practice
This article will introduce how to mount configuration files for components in Rainbond and share configuration files between multiple components. It is suitable for scenarios where multiple components need to use the same configuration file, which can be shared directly without editing the settings multiple times; The shared configuration file will only resolve the environment variables of the current component; the following will take MariaDB as an example to demonstrate the use of configuration files.
Overview
Rainbond combines the configuration files implemented by Kubernetes' ConfigMap. It is a special storage type that allows users to directly define file content, usually referred to as configuration files; configuration files have two major characteristics:dynamic rendering environment variables and configuration file sharing.
The official mirror of MariaDB , which gives two ways to customize the configuration file
- The first
There needs to be a configuration file on the host, and this configuration file is mounted to the /etc/mysql/conf.d directory of the container when the container starts, and the configuration file under/etc/mysql/conf.d That will overwrite the default configuration file /etc/mysql/my.cnfin the container.
This method is not flexible enough to confirm which node the Pod will be scheduled on when the component is created (the data center is usually a cluster). It is necessary to mount the configuration file after the component is created, and then restart the component to make it take effect.
- the second
Pass the relevant parameters in the docker run command when the container is started, for example, modify the default encoding and collation rules through the two parameters of character-set-server and collation-server:
docker run --name some-mariadb -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mariadb:tag --character-set-server=utf8mb4 --collation-server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
This method is also inflexible. If you set a lot of parameters, the docker run command will be very long.
How to configure Rainbond
Rainbond combines the configuration file implemented by ConfigMap of k8s. This method is relatively flexible. It can dynamically render environment variables and share it with other components. The following demonstrates Rainbond's configuration file mounting and sharing configuration file methods.
Preconditions
- You can connect to the external network, pull the GitHub code, use the source code to build MariaDB project, and set the subdirectory to 10.5;
- Have a MariaDB configuration file.
Configuration file example
# MariaDB-specific config file.
# Read by /etc/mysql/my.cnf
[client]
# Default is Latin1, if you need UTF-8 set this (also in server section)
default-character-set = ${DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET:utf8}
[mysqld]
#
# * Character sets
#
# Default is Latin1, if you need UTF-8 set all this (also in client section)
#
character-set-server = ${CHARACTER_SET_SERVER:utf8}
collation-server = ${COLLATION_SERVER:utf8_general_ci}
character_set_server = ${CHARACTER_SET_SERVER:utf8}
collation_server = ${COLLATION_SERVER:utf8_general_ci}
default_storage_engine = ${DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE:innodb}
# Import all .cnf files from configuration directory
!includedir /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/
Configuration file explained
In this configuration file, dynamic rendering configuration files are used to parse environment variables, DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET, CHARACTER_SET_SERVER,DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE and other variables that can parse environment variables are set, and default values are set for them, if they exist in the component If the specified environment variable is specified, Rainbond will parse the value of the environment variable into the configuration file; if the environment variable does not exist in the component, then Rainbond will parse the default value into the configuration file; if the specified environment variable does not exist, and If no default value is set, then Rainbond will not parse.
Syntax for dynamic rendering configuration file parsing environment variables:
${环境变量名}
${环境变量名:默认值}
Steps
- Create MariaDB components from source code, do not check build and start when creating
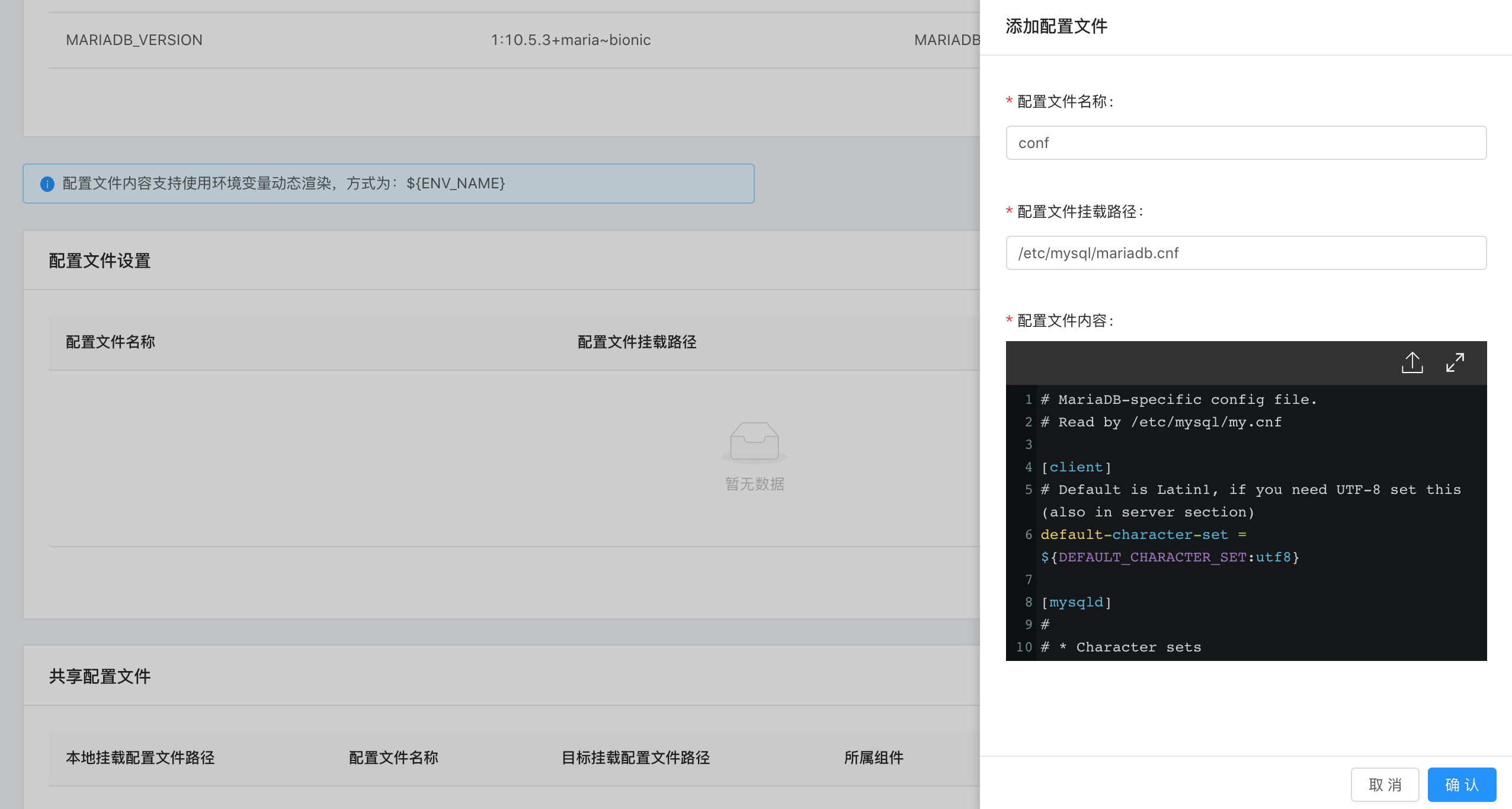
- On the component management page environment configuration --> configuration file settings , click to add configuration file , use the above example configuration file, and the mount path is
/etc/mysql/mariadb.cnf; as shown in the figure Show:
- Add environment variables
On the component management page environment configuration --> custom environment variables --> add variables add environment variables for components DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE=myisam and MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=rainbond
Show results
- Build the MariaDB component and enter the container to check the contents of
/etc/mysql/mariadb.cnfafter successful startup
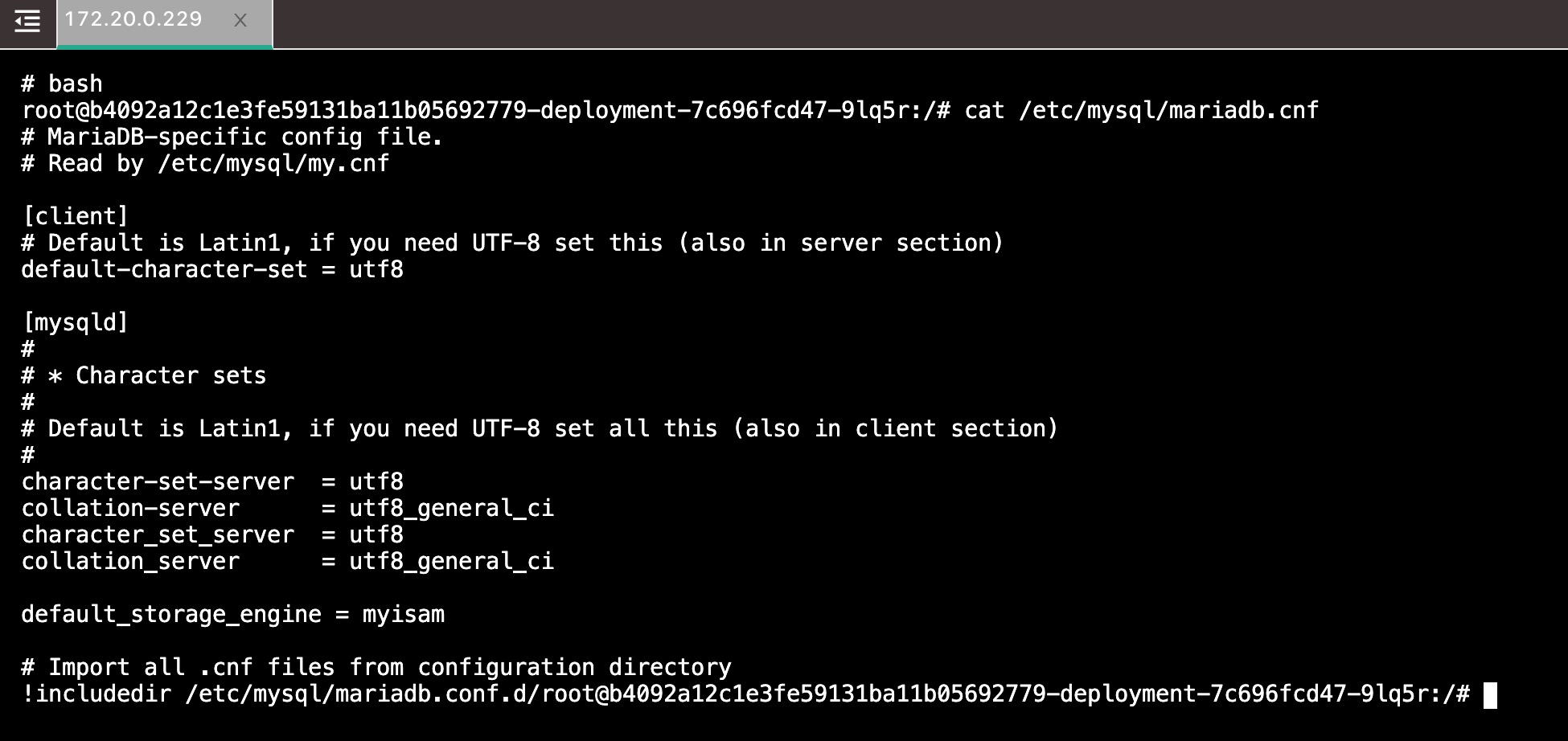
It can be found that Rainbond does not find DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET,CHARACTER_SET_SERVER and other variables that do not have corresponding environment variables, and uses their corresponding default values for analysis; finds the environment variables corresponding to DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE , then use the environment variable DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE The value myisam is parsed.
- Log in to MySQL to see if the configuration takes effect:
# 登录 MySQL
root@gr52b3ee-0:/# mysql -uroot -prainbond
# 检查编码和校对规则
MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like "%character%";
+--------------------------+----------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+----------------------------+
| character_set_client | utf8 |
| character_set_connection | utf8 |
| character_set_database | utf8 |
| character_set_filesystem | binary |
| character_set_results | utf8 |
| character_set_server | utf8 |
| character_set_system | utf8 |
| character_sets_dir | /usr/share/mysql/charsets/ |
+--------------------------+----------------------------+
# 查看存储引擎
MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW STORAGE ENGINES;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| MRG_MyISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | Stores tables as CSV files | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | DEFAULT | Non-transactional engine with good performance and small data footprint | NO | NO | NO |
| Aria | YES | Crash-safe tables with MyISAM heritage | NO | NO | NO |
| InnoDB | YES | Supports transactions, row-level locking, foreign keys and encryption for tables | YES | YES | YES |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| SEQUENCE | YES | Generated tables filled with sequential values | YES | NO | YES |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
It can be seen that the encoding, proofreading rules, and storage engine settings have all taken effect.
Configure file sharing
Preconditions
The configuration file has been mounted for MariaDB with the above steps
Steps
- Recreate a MariaDB component,
- In the component management interface environment configuration --> shared configuration file --> mount shared configuration file find the MariaDB configuration file above and fill in the mount path, update the component, as shown in the figure:

Show results
After the creation is complete, enter the container to view the configuration file/etc/mysql/mariadb.cnfThe content is as follows:
# MariaDB-specific config file.
# Read by /etc/mysql/my.cnf
[client]
# Default is Latin1, if you need UTF-8 set this (also in server section)
default-character-set = utf8
[mysqld]
#
# * Character sets
#
# Default is Latin1, if you need UTF-8 set all this (also in client section)
#
character-set-server = utf8
collation-server = utf8_general_ci
character_set_server = utf8
collation_server = utf8_general_ci
default_storage_engine = innodb
# Import all .cnf files from configuration directory
It can be seen that since the current component does not set the DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE variable, Rainbond uses its default value innodb for parsing, and other configurations have taken effect.