Component-dependent port conflict handling
When we deploy a distributed business with multiple services, we must consider how to deal with the communication between services, so when we deploy the business to Rainbond, how do we deal with it?
Rainbond's out-of-the-box ServiceMesh architecture uses Sidecar proxy by default, which transparently solves the communication problem between components in distributed scenarios.
For example, if component A needs to access component B, you can make component A depend on component B, so that component A will start an envoy service as a plug-in at the same time when it starts, and the envoy service will map the inbound port of component B to component A in the Pod network space. The same port of the local loopback address127.0.0.1, that is to say, the B component has opened the internal port 8080, then after the dependency relationship between A and B is established, accessing127.0.0.1:8080in the A component will Relevant requests are forwarded by envoy to port 8080 of the B component.
But there is often a situation in our actual business, that is, a component needs to communicate with multiple other components, and the service ports used by these components may be the same, which will cause envoy to return to the local loopback address127.0.0.1port conflict occurred while listening.
We can solve this problem in two ways:
Mode:Port multiplexing through HTTP 7-layer network management
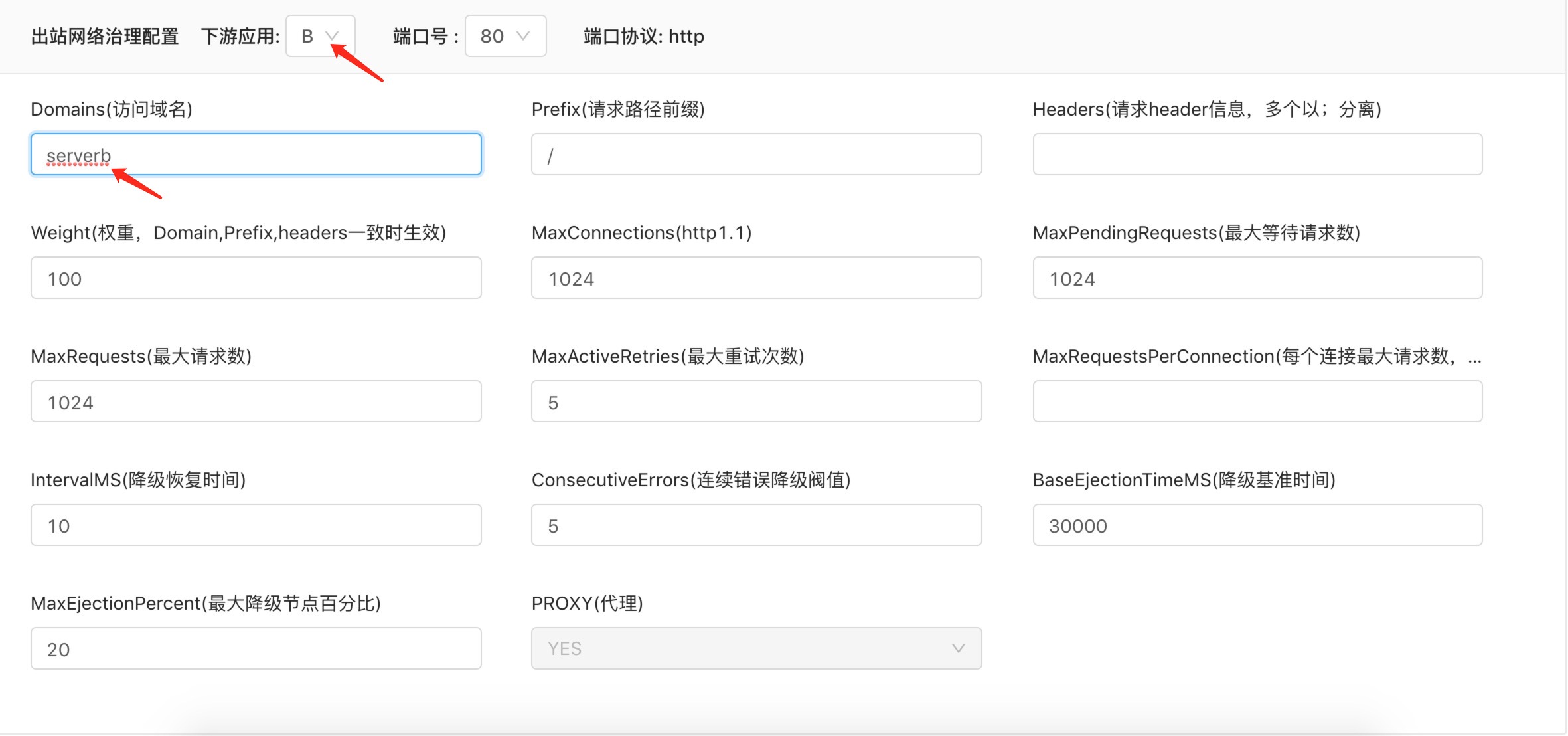
For this type of component, the domain name (Domain), request path, request header and other routing conditions of the downstream component are set through thenetwork management plug-in, and envoy forwards the request to access the corresponding domain name to the corresponding back-end component port through port 80. The corresponding port of the component network space where the plug-in is activated is no longer monitored. The specific configuration process is as follows:
build dependencies
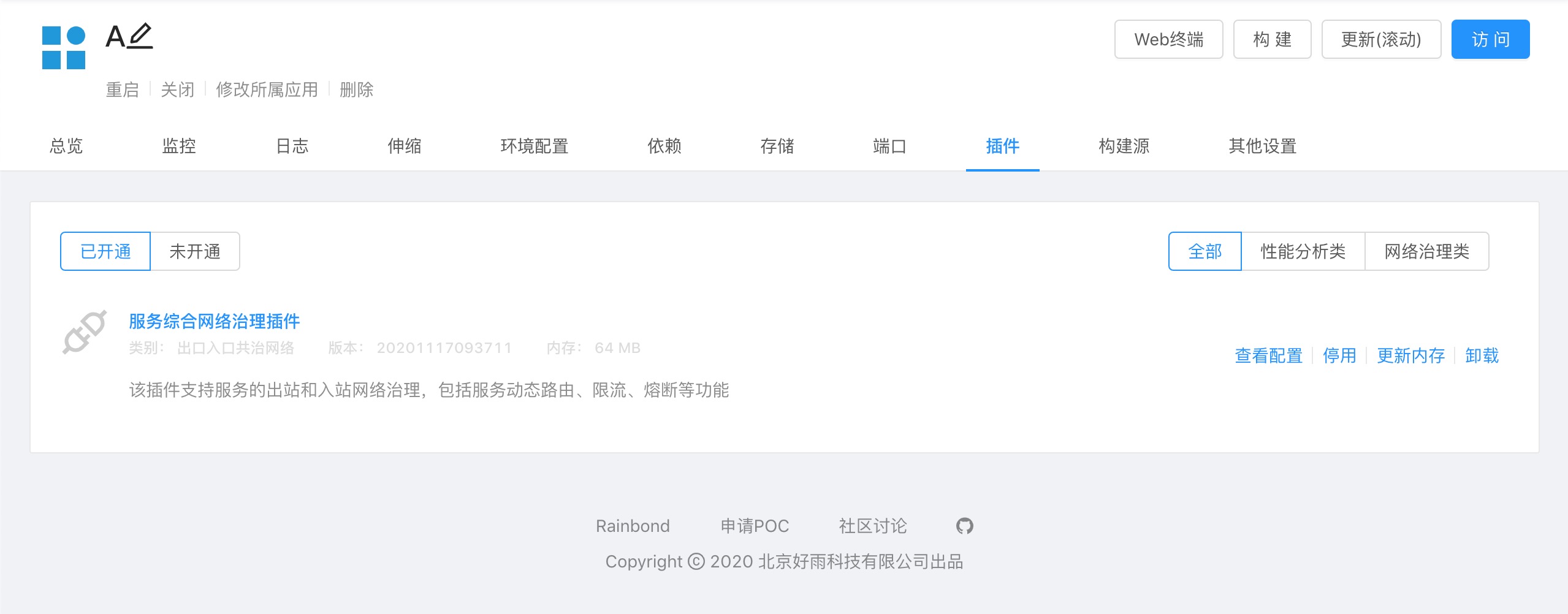
Activate the A component network management plug-in
Configure the downstream service access domain name
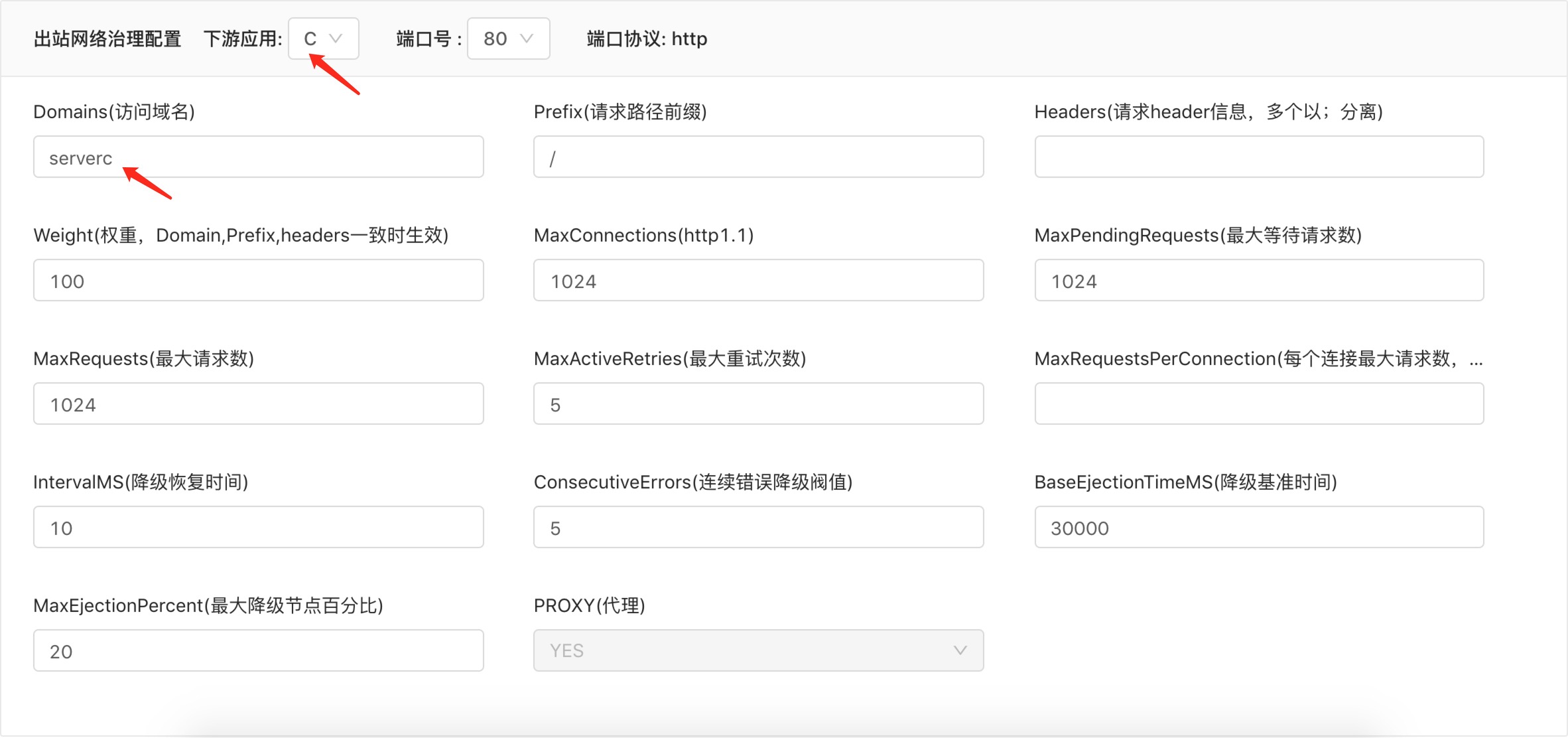
Update components and test the effect of domain name access

Precautions
The network management plug-in will listen to
127.0.0.1:80of the service network, so if the A component itself listens to port 80, there will be an abnormal operation of the component status due to the fact that port 80 is already occupied and the service cannot be started.
Method:Dynamically change the listening port of the component
The component running on Rainbond will automatically inject an environment variablePORTat startup, the value of which is the first port set by the component. You can set the component to refer to thePORTvariable to set the listening port of the service when the component starts, and set the listening port of the service by Platform control, you can monitor port changes without modifying the code.In this way, different services depend on different ports to avoid conflicts. Taking the source code construction ofJavaproject as an example, the specific configuration process is as follows:
Set build source start command to
web: java -Dserver.port=$PORT $JAVA_OPTS -jar target/*.jar
Add component ports and build components.
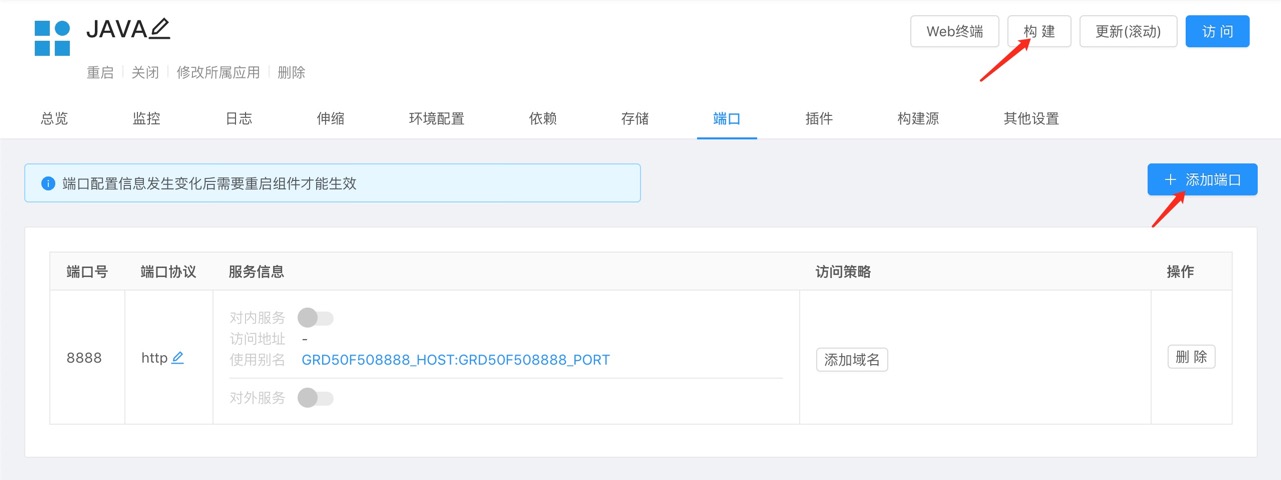
Verify service listening port
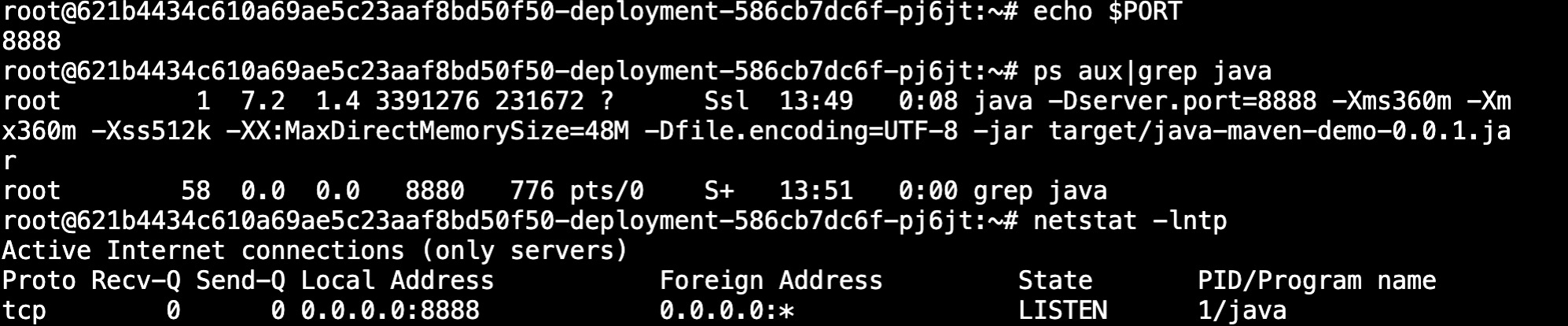
Different development languages and middleware have different ways of setting the listening port. Developers need to make development and configuration according to the actual setting method.
Method 30:Use the Kubernetes native Service governance mode
In the upcoming 5.3 version of Rainbond, it will support the direct use of the Kubernetes native Service mode and provide a friendly configuration method. In this network governance mode, each internal port can set a custom access domain name, which will be generated after the setting. Corresponding Service resources, so that components can be accessed directly through the internal domain name + port, and envoy is no longer used for port proxying, which fundamentally avoids the problem of port conflicts.
Method 40 Using the:Network Governance Model
In subsequent versions of Rainbond, Istio network governance modewill also be supported. In this network governance mode, only the fixed Pod port configured by Istio will be monitored, not the component ports that need to be accessed, and other components that need to be accessed. Traffic rules and configurations will be set by Pilot and then forwarded by Envoy through 15001/15006.